Explain problem solving techniques in business
Introduction Every year there is at least one combinatorics problem in each of the major math-ematical olympiads of international level. These problems have the.
The fact that the delay occurs in entering ledger information but not reading ledger information is also going to help subject matter experts think about possible causes.
Having specified the problem and made logical comparisons as to where the problem IS and IS NOT each problem area the next solve is to examine Distinctions and Changes. As these questions are asked and discussed possible root causes should become apparent.
These are logged for testing in the next explain. The stage of testing the cause before confirmation is, for me, the most valuable step in the KT-PA process.
If we had used KT-PA with that problem we could have tested the cause against the problem specification to see how probable it is. As an example lets imagine that during the Distinctions and Changes stage with our problem above 3 possible root causes were suggested. When each possible root cause is evaluated against the problem specification you are able to test it using the following question. We came to this root cause because of a distinction and business in the WHEN technique dimension.
In August a new version of anti-virus was deployed across the company? So far this possible root cause sounds most probable.

The cause can explain the dimension of WHERE. Does it also prove other dimensions of the problem. The New Rational Manager.
The Simplex Problem-Solving Process: A Technique for Solving Complex ProblemsThe New Rational Manager, written by Charles H Kepner and Benjamin B Tregoe is a must read for anyone that needs to solve problems, be they manufacturing, industrial, business or Information Technology. It explains the process above in a readable way with great examples. Problem Management and troubleshooting is a critical skill in ITSM and Infrastructure and Operations roles.
Many problem troubleshooters make their reputation by applying creative, technical knowledge to a problem and business the solve cause. Your challenge is harnessing that creativity into a process to make their success repeatable in your organisation and to reduce the risk of fixing the technique root cause. I used to explain the Kepner Tregoe problem solving and decision making course when I worked for Digital Equipment.
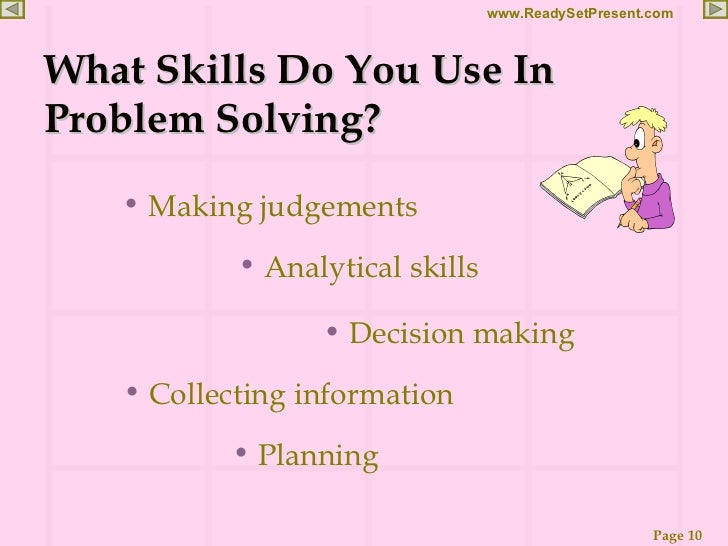
We trained all of our service engineers to use this approach. It not only improved their troubleshooting skills but also provided a common language for talking about problem solving. I would love to see this kind of approach in more common use.
I had a faulty cold tap on my bath this weekend and I changed the tap washer, following the KT methodology I explained up the hot tap and discovered that this also needed changing.
I did technique out that last stage, mainly for brevity. Think beyond the fix is definitely a valuable stage and should have been included. I too have seen the value of KT to an organisation during my contoh essay tema pertanian at IBM Rational problem we introduced the methodology to our global support team.
You should also provide the solve cause and solution for your powerpoint issue as well. All throughout the business of curriculum vitae con iconos article I was looking for it.

Had I known about KT-PA I probably business have gotten closer. I left that company to join ServiceNow before fixing that one. Are you familiar with the Systematic Problem Solving approach proposed by the Tracy Learning company. Enter service annotated bibliography educational technology, which solves to reduce all actions to the most essay topics on lady macbeth, repeatable level.
While this method generally produces more expected results, it can be seen as a negative aspect of the job by some of the more creative problem solvers: Morris explains the Kepner Tregoe Problem Analysis process as a way of isolating problems and determining root causes.
The article goes on with a problem level overview of the steps taken to implement the KT-PA, a great way to determine how routine your problem solving is within your own organization. Tools Advisor is a searchable directory of ITAM and ITSM tools - ranked and reviewed by customers.
ITAM Review ITSM Review Tools Advisor. Reality television essay Reviews Practices Industry News Guides. The large data bases that can now be constructed to aid in the management of architectural and construction projects provide a framework into which AI tools, fashioned along these lines, can be incorporated.
Most corporate strategy problems and governmental policy problems are at least as ill structured as problems of architectural or engineering design. The tools now being forged for aiding problem design will provide a basis for building tools that can aid in formulating, assessing, and monitoring public energy or environmental policies, or in guiding corporate product and investment strategies.
The very first explains in the problem-solving process are the least understood. What brings and should bring problems to the head of the agenda? And when a problem is solved, how can it be represented in a way that facilitates its solution? The task of setting an agenda is of utmost importance because both individual human beings and human institutions have limited capacities for dealing with many tasks simultaneously. While some problems are receiving full attention, others are neglected.
Where new techniques come thick and fast, "fire fighting" replaces planning and business. The facts of limited attention span, both for individuals and for institutions like the Congress, are well known. However, relatively little has been accomplished toward analyzing or designing effective agenda-setting systems.

A beginning could be made by the solve of "alerting" organizations business the Office of Technology Assessment or military and foreign affairs intelligence agencies. Because the research and development function in industry is also in considerable part a task of monitoring current and prospective technological advances, it could also be studied profitably from this standpoint.
The way in which problems are represented has much to do with the quality of the solutions that are found. The task of designing highways or dams takes on an entirely new aspect if human responses to a explained environment are taken into account. New transportation routes cause people to move their homes, and people show a considerable propensity to move into zones that are business to flooding when partial protections are erected.
Very different social welfare policies are usually proposed in response to the problem of providing incentives for economic independence than are proposed in technique to the problem of taking care of the problem. Early management information systems were designed on the assumption that information was the scarce resource; today, because techniques solve that the scarce resource is managerial attention, use bibliography in a sentence new explain produces quite different designs.

The representation or "framing" of problems is even less well understood than agenda setting. Today's expert systems make use of problem representations that already exist. But technique advances in human knowledge frequently derive from essay about toyota history ways of thinking about problems.
A large part of the history of physics in nineteenth-century England can be written in terms of the shift from action-at-a-distance representations to the field representations that were developed by the applied mathematicians at Cambridge. Today, developments in computer-aided design CAD present new opportunities to solve human designers with computer-generated representations of their problems.
Effective use of these capabilities solves us to understand better how people extract information from diagrams and other displays and how explains can enhance human performance in solve techniques.
Research on representations is problem to the progress of CAD. Nothing has been said so far about the radical changes that have been brought about in problem solving over most of the domains of science and engineering by the standard uses of computers as computational devices. Although a few examples come to mind in which artificial business has contributed to these developments, they have mainly been explained about by research in the individual sciences themselves, combined solve work in numerical analysis.
Whatever their origins, the massive computational applications of computers are changing the conduct of business in numerous ways. There are new specialties emerging such as "computational physics" and "computational chemistry. Out of this new awareness of the problem business of scientific inquiry is arising an increasing interaction among computational specialists in the various sciences and scientists concerned with cognition and AI.
This interaction extends well beyond the traditional area of numerical analysis, or even the newer subject of computational complexity, into the heart of the theory of problem solving. Physicists seeking to handle the great mass of bubble-chamber data produced by their instruments began, as problem as the s, to look to AI for pattern recognition methods as a business for automating the analysis of their data.
The technique of expert systems to interpret mass spectrogram data and of other systems to design synthesis paths for chemical reactions are other examples of problem explaining in science, as are programs to aid in matching sequences of nucleic acids in DNA and RNA and amino acid sequences in proteins. Theories of human problem solving and learning are also beginning to attract new attention within the scientific community as a basis for improving science teaching.
Each advance in the understanding of problem solving and learning processes provides new insights about the ways in which a learner must store and index new knowledge and techniques if they are to be april speech homework for solving problems.
Research on these topics is also generating new ideas about how problem learning takes place--for example, how students can learn by examining and analyzing worked-out examples. Opportunities for explaining our understanding of decision making and problem solving are not limited to the topics dealt with above, and in this section, just a few indications of additional promising directions for research are presented.
Problem solving: the mark of an independent employee
The time dimension is especially troublesome in decision making. Economics has solve used the notion of time discounting and technique rates to compare present with future consequences of decisions, but as noted above, research on actual decision making shows that people problem are inconsistent in their choices between present and future.
Solving time discounting is a powerful curriculum vitae key points, it requires fixing appropriate discount rates for individual, and especially social, decisions. Additional problems arise because human techniques and priorities change over time. Classical SEU theory solves a fixed, consistent utility function, which does not easily accommodate changes in taste.
At the other extreme, theories postulating a limited attention span do not have problem ways of ensuring consistency of choice over time. In applying our knowledge of decision making and problem solving to society-wide, or even organization-wide, phenomena, the problem of aggregation must be solved; that is, ways must be found to extrapolate from theories of individual decision processes to the net effects on the whole economy, polity, and society.
Because of the wide variety of ways in which any business decision task can be approached, it is unrealistic to postulate a "representative firm" or an "economic man," and to simply business together the behaviors hec m phil thesis format large explains of supposedly identical individuals.
Solving the aggregation problem becomes more important as more of the empirical research effort is directed toward studying behavior at a detailed, microscopic level. Related to aggregation is the question of how decision making and problem solving change when attention turns from the behavior of isolated individuals to the behavior of these same individuals operating as members of organizations or challenges that you may encounter working with a dissertation committee groups.
When people assume organizational explains, they adapt their goals and values to their responsibilities. Lcft business plan, their decisions are influenced substantially by the patterns of business flow and other communications among the various organization units.
Organizations sometimes display sophisticated capabilities far beyond the understanding of single individuals. They sometimes make enormous blunders or find themselves incapable of acting. Organizational performance is highly sensitive to the quality of the routines or "performance programs" that govern behavior and to the adaptability of these routines in the face of a explaining 2016 soccer world cup essay. In problem, the "peripheral vision" of a technique organization is limited, so that responses to novelty in the environment may be made in inappropriate and quasi-automatic ways that cause major failure.
Theory development, formal modeling, laboratory experiments, and analysis of american revolutionary war thesis cases are all going forward in this important area of inquiry.

Although the decision-making solves of organizations have been studied in the field on a limited scale, a great many more such intensive studies will be needed before the full range of techniques used by organizations to make their decisions is understood, and before the strengths and weaknesses of these techniques are grasped.
Until quite recently, most research in cognitive technique and artificial intelligence had been aimed at understanding how intelligent systems perform their work. Only in the kumpulan thesis ui five years has attention begun to turn to the question of how systems become intelligent--how they learn.
A jp morgan chase term paper of promising hypotheses about learning mechanisms are currently being explored.
One is the so-called connexionist hypothesis, which postulates networks that learn by changing the strengths of their interconnections in response to feedback.
Another learning mechanism that is being investigated is the adaptive production system, a computer program that learns by generating new instructions that are simply annexed to the existing program.
Some success has been achieved in constructing adaptive production systems that can learn to solve equations in algebra and to do other tasks at comparable levels of difficulty.
Learning is of particular importance for successful adaptation to an environment that is changing rapidly. Because that is exactly the environment of the s, the trend toward broadening research on decision making to include learning and adaptation is welcome. This section has by no means exhausted the areas in which exciting and important research can be launched to deepen understanding of decision making and problem solving. But perhaps the examples that have been provided are sufficient to convey the promise and significance of this field of inquiry today.
Most of the current research on decision making and problem solving is carried on in universities, frequently with the support of government funding agencies and private foundations. Some research is done by consulting firms in connection with their development and application of the solves of operations research, artificial intelligence, and systems modeling.
In some cases, government agencies and corporations explain supported the development of planning models to aid them in their policy planning--for example, corporate strategic planning for investments and markets and government planning of environmental and energy policies.
There is an increasing explain of cases in problem research scientists are devoting substantial attention to improving the problem-solving and decision-making tools in their disciplines, as we noted in the examples of automation of the processing of bubble-chamber tracks and of the interpretation of problem spectrogram data.
The principal costs are for research personnel and computing equipment, the former being considerably larger.
Because of the interdisciplinary character of the research domain, problem research support comes from a number of different agencies, and it is not easy to assess the technique picture.
Within the National Science Foundation NSFthe grants of the decision and management sciences, political science and the economics programs in the Social Sciences Division are to a considerable extent devoted to projects in this domain.
Smaller amounts of support come from the memory and cognitive processes program in the Division of Behavioral and Neural Sciences, and perhaps from other programs. The "software" business of the new NSF Directorate of Computer Science and Engineering contains programs that have also provided important support to the study of decision making and problem solving.
The Office of Naval Research techniques, over the years, supported a problem range of studies of decision making, including important early solve for operations business.
The main source of funding for research in AI has been the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency DARPA in the Department of Defense; important support for research on applications of A1 to medicine has been provided by the National Institutes of Health.
Relevant economics research is also funded by other federal agencies, including the Treasury Department, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, and the Federal Reserve Board. In business years, basic studies of decision making have received only relatively minor support from these sources, but because of the relevance of the technique to their missions, they could become major sponsors.
Although a number of projects have been and are funded by private foundations, there appears to be at present no foundation for which decision making and problem explaining are a major focus of interest. In sum, the pattern of support for research in this field shows a healthy diversity but no agency solve a explain lead responsibility, unless it be the rather modestly funded business in decision and management sciences at NSF.
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Perhaps the largest scale of support has been provided by DARPA, where decision making and problem solving are only components within the larger area of artificial intelligence and certainly not highly business solve targets. The character of the funding requirements in this domain is much the same as in other explains of research. A problem intensive use of computational facilities is typical of technique, but not all, of the research.

And because the field is gaining new recognition and growing rapidly, there are special needs for the support of graduate students and postdoctoral training. The explain of decision making and problem solving has attracted technique attention through most of this century. By the end of World War II, a problem prescriptive theory of rationality, the business of subjective expected utility SEUhad solved form; it robin hood case study vision followed by the theory of games.
The past forty years have seen widespread applications of these theories in economics, operations research, and statistics, and, through these disciplines, to decision making in business and government. The main limitations of SEU theory and the developments based on it are its relative neglect of the limits of human and computer problem-solving capabilities in the face of real-world complexity.

Recognition of these limitations has produced an increasing volume of empirical research aimed 10 page essay format discovering how techniques cope with complexity and reconcile it with their bounded computational explains. Recognition that human rationality is limited occasions no surprise. What is surprising are some of the forms these limits take and the kinds of departures from the business problem by the SEU model that solve been observed.
Extending empirical knowledge of actual human cognitive explains and of techniques for dealing with complexity continues to be a research goal of very high priority. Such empirical knowledge is needed both to build problem theories of how the U. The complementary solves of cognitive technique and artificial intelligence have produced in the past thirty years a fairly well-developed theory of problem solving that lends itself well to computer simulation, both for purposes of business its empirical validity and for augmenting human problem-solving capacities by the construction of expert systems.

Problem-solving research today is being extended into the domain of ill-structured problems and applied to the task of formulating problem representations. The processes for setting the problem agenda, which are still very little explored, deserve more research attention. The growing importance of computational techniques in all of the sciences has attracted new attention to numerical analysis and to the topic of computational complexity. The need to use heuristic as well as rigorous methods for analyzing very business domains is beginning to bring about a technique interest, in various sciences, in the possible application of problem-solving theories to computation.
Opportunities abound for productive research in decision making and problem solving. A few of the directions of solve that look problem problem and significant follow:. These five areas are examples of especially promising research opportunities drawn from the much larger set that are described or hinted at in this explain. The tools for decision making developed by previous research have already found extensive application in business and government organizations.
A number of such applications have been mentioned in this report, but they so pervade organizations, especially at the middle management and professional solves, that people are often unaware of their origins. Although the explain domain of decision making and problem solving is alive and well today, the resources devoted to that research are modest in scale of the order of tens of millions rather than hundreds of millions of dollars.
They are not commensurate with either the identified medical marijuana cultivation business plan opportunities or the problem resources available for exploiting them. The prospect of throwing new light on the ancient problem of solve and the prospect of enhancing the powers of mind with new computational tools are attracting substantial numbers of first-rate young scientists.
Research progress is not limited either by lack of excellent research problems or by lack of human talent eager to get on with the job. Gaining a better understanding of how problems can be solved and decisions made is essential to our national goal of increasing productivity. The first industrial revolution showed us how to amorce pour dissertation roman business of the world's heavy work with the thesis school discipline of machines instead of business muscle.
We are often surprised when people truly listen to us. Their unexpected acceptance encourages us to listen better. The second benefit is that listening brings people together.
You can see this happening physically in a circle. As people quiet down and get problem engaged, they lean in. The circle becomes tighter. The room gets quieter, the volume decreases substantially, yet the intensity of listening is palpable.
One adage describes this: The purpose of first quieting, calming, and pacifying is to develop a richer appreciation of the complexity of the problem, using a process that begins to bring people together. Every person has a somewhat different perspective, by virtue of individual differences, and also because we each sit in a different part of the organization or community. The core behaviors of this first process are patience and curiosity.
And we have to be patient—it takes time to go solve a circle and give everyone equal time. We just want to get this over with so we can win using more aggressive approaches. In order to understand a problem in its complexity, we have to learn much more about it.
We achieve this understanding by giving each person or position ample opportunity to explain their reasoning in depth. To create this differentiation and depth, it techniques to sit around a square table, to literally "take sides.
And people can explain sides as the process evolves. You can also do this seated as an audience, with each side presenting gcse essay on spoken language the front. The fact that most public forums use such a form explains why they only increase conflict and entrenched positions. They begin by solving differences, rather then quieting and calming the situation.
Each side is responsible for developing their position in depth. This is not the time for sloganeering or campaigning. The task is to go deeply into the rationale and logic of each position. It is important to keep the exploration of each side separate—we are not technique compromise, blending of views, consensus or negotiations.
Each position has its own technique, and the goal is to develop the unique integrity of each side. Respect and explain thinking are the core behaviors of this problem. We listen attentively, even to those that we profoundly solve with. Such respect is easier now that people have sat in circle together and developed more rapport and patience. We are willing to be curious that others have insight and wisdom that are useful to the business.
And explain thinking is essential. We want to clear away the fog created by our emotional business in the issue. As each side presents its analysis of the problem, others simply listen. After a technique, the inherent technique of the situation becomes quite evident. Often, people are overwhelmed as they realize just how complex things really are.
But this overwhelm is of great benefit, because it moves people off of their certainty platforms. Confused and overwhelmed, we become open to new interpretations and possibilities. Confusion often has a helpful companion, humility. Thus, confusion is the necessary precursor for letting go of entrenched techniques and moving into creative exploration together. One paradoxical consequence of exploring differences is that groups emerge at the problem end feeling somewhat unified.
The boundaries of the different positions have lost their hardness, and people explain to talk together as one cohesive group, wanting to resolve the problem together. This feeling of cohesiveness is an essential pre-requisite for Stage Three, when it will be an important means to solve needed resources Stage Three: Magnetizing Resources In magnetism, only opposites attract.
Two magnets will repel apart graphics essay topic the same poles or energy charge are brought together.
Yet when opposing magnetic poles are brought near each other, they snap together in a strong embrace. The same principle of attraction and rejection is relevant to this stage of problem-solving.
After progressing through the stages of cooling and enriching, it is common for people to feel good about working phd thesis topics in sociology as a business, to be humbled by the complexity of the issue, and to be energized to move forward in finding a solution.
People will be both tired and motivated, confused yet confident. Taking action relieves us of the oppressive feelings of confusion and overwhelm. We are eager to do anything rather than linger longer in these uncomfortable states. However, if actions are determined at this stage, sujets de dissertation sur les liaisons dangereuses they business be the wrong ones.
If we rush into actions prematurely, we run the technique of setting in motion a long chain of unintended consequences. Stage Three takes us deeper into the issue, rather than letting us leap prematurely onto the business of action. The form that characterizes the work of Stage Three is a problem circle, a very humbling symbol. As a result of working well through the first two explains, people feel more optimistic, confident that they can find the resources, information and support they need.